
Base-8 is great for fiber optic links
Receive Corning's newly published article in DatacenterDynamics, “Base-8 is great for fiber optic links.” Learn the difference between base-2, base-8 and base-12 architectures, and understand how network trends are impacting data center design in the future.
Excerpt:
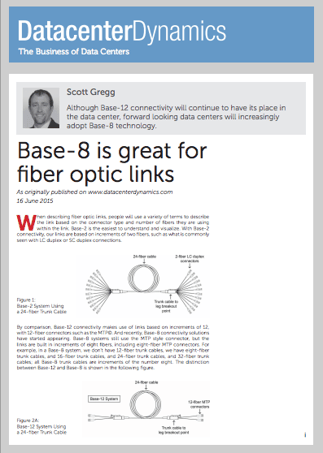
When describing fiber optic links, people will use a variety of terms to describe the link based on the connector type and number of fibers they are using within the link. Base-2 is the easiest to understand and visualize. With Base-2 connectivity, our links are based on increments of two fibers, such as what is commonly seen with LC duplex or SC duplex connections.
By comparison, Base-12 connectivity makes use of links based on increments of 12, with 12-fiber connectors such as the MTP©. And recently, Base-8 connectivity solutions have started appearing. Base-8 systems still use the MTP style connector, but the links are built in increments of eight fibers, including eight-fiber MTP connectors. For example, in a Base-8 system, we don’t have 12-fiber trunk cables, we have eight-fiber trunk cables, and 16-fiber trunk cables, and 24-fiber trunk cables, and 32-fiber trunk cables; all Base-8 trunk cables are increments of the number eight. The distinction between Base-12 and Base-8 is shown in the following figure.


.png?width=58&height=58&name=X_logo_2023_(white).png)
